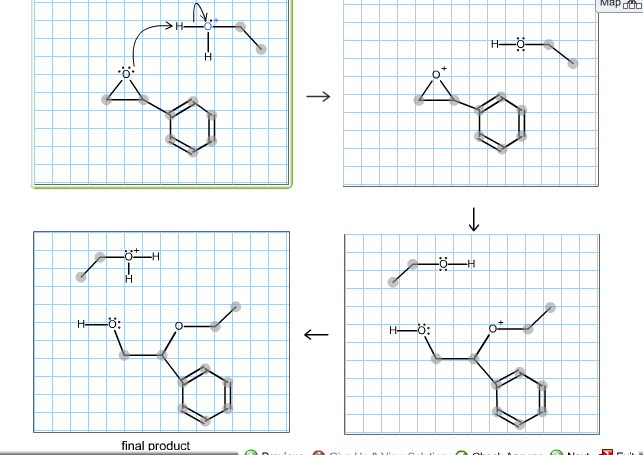
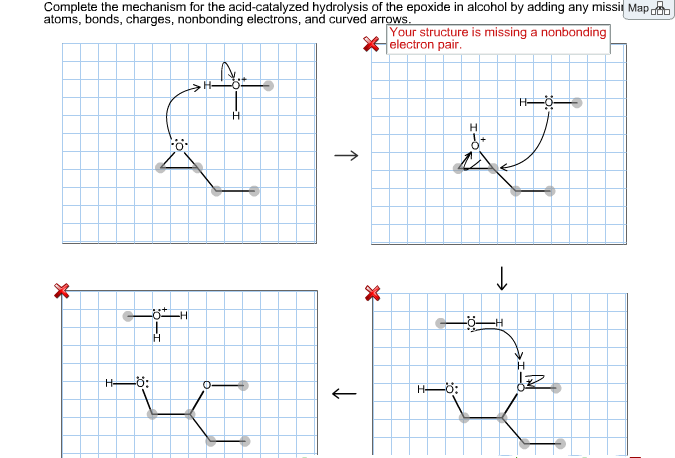
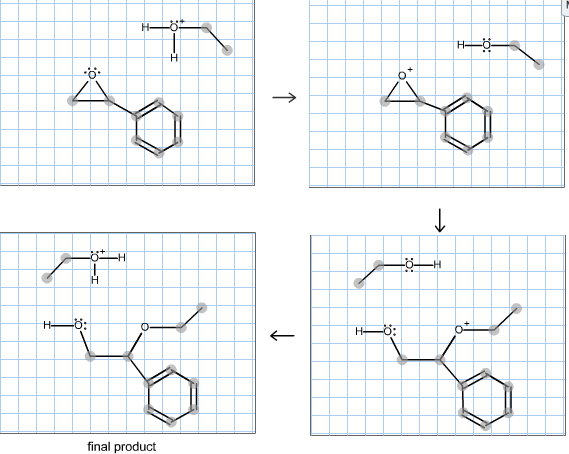
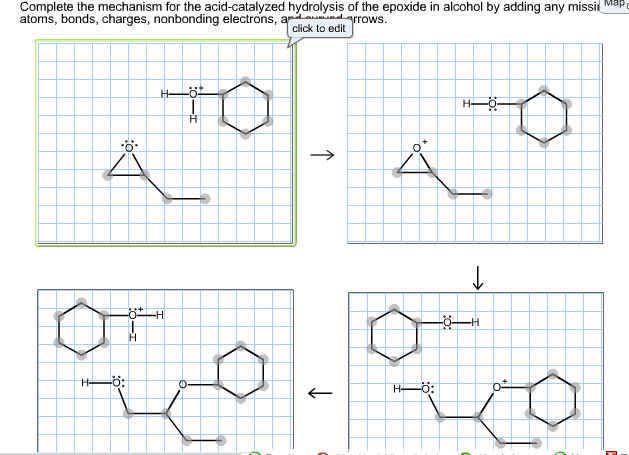
A lone pair of electrons from the oxygen atom of the alcohol forms a bond with the carbonyl carbon breaking its pi bond with the other oxygen. The hydroxide ion attacks one of the carbon atoms in the epoxide in an SN2 displacement reaction.
Complete The Mechanism For The Acid Catalyzed Hydrolysis Of The Epoxide In Alcohol - If you're searching for picture and video information linked to the key word you've come to visit the right blog. Our site gives you hints for viewing the highest quality video and image content, search and find more informative video articles and images that match your interests. comprises one of tens of thousands of video collections from various sources, especially Youtube, therefore we recommend this movie for you to view. This blog is for them to stop by this site.
Complete The Mechanism For The Acid Catalyzed Chegg Com
The result is anti-hydroxylation of the double bond in contrast to the syn-stereoselectivity of the earlier method.
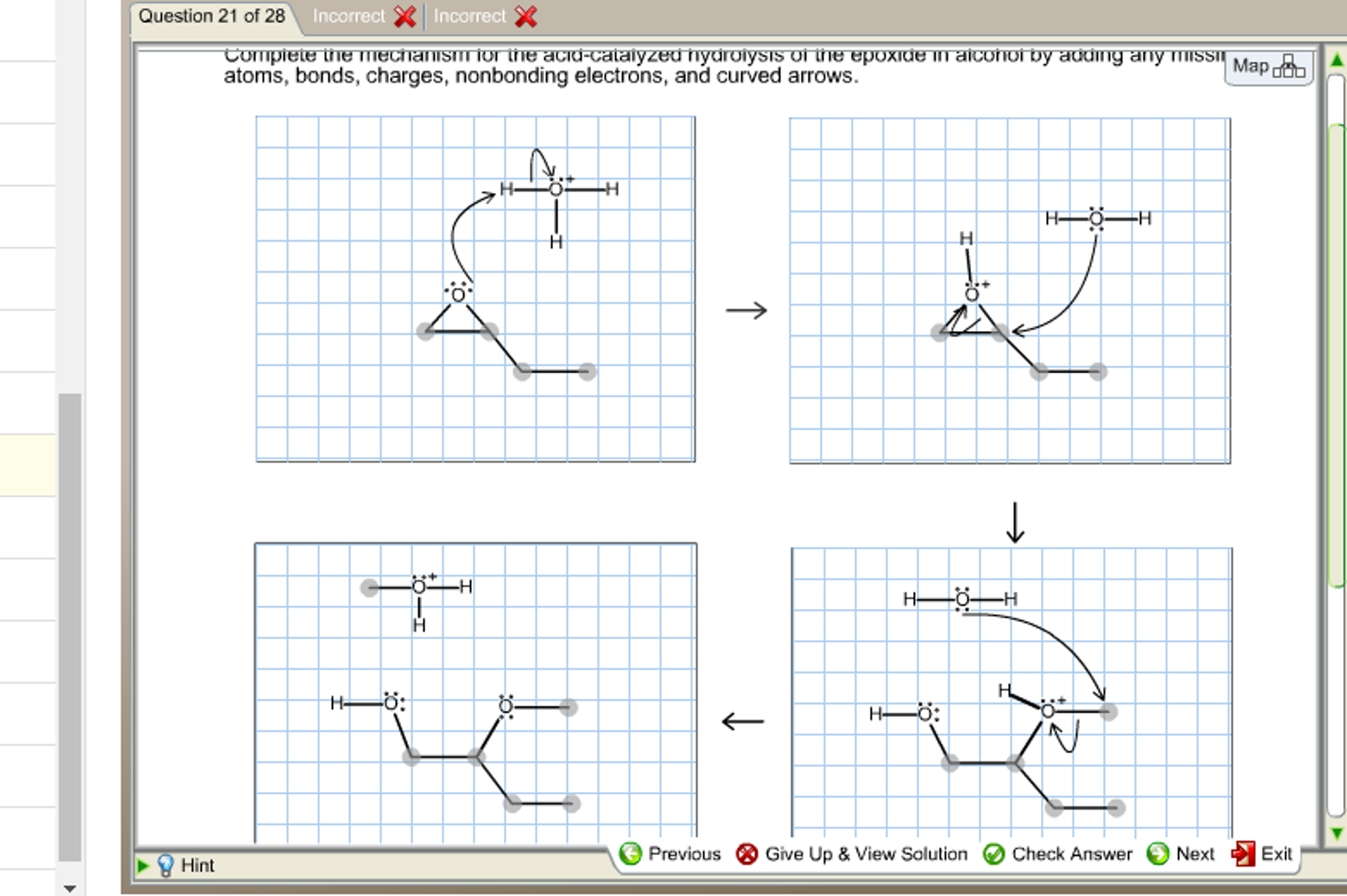
Complete the mechanism for the acid catalyzed hydrolysis of the epoxide in alcohol. The epoxidation of ethylene involves its reaction with oxygen. Complete the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of the epoxide in alcohol by adding any missing atoms bonds charges nonbonding electrons and curved arrows. It doesnt affect the argument but in fact all the steps are reversible.
Acetal Hydrolysis Mechanism We have learned that the reactions of aldehydes and ketones with alcohols and amines are all reversible and one application of this feature was the use of acetals as protecting groups for aldehydes and ketones. All of the hydrogen atoms in the phosphoricV acid are fairly positively charged because they are attached to a very electronegative oxygen atom. Ethyl ethanoate is heated under reflux with a dilute acid such as dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sulphuric acid.
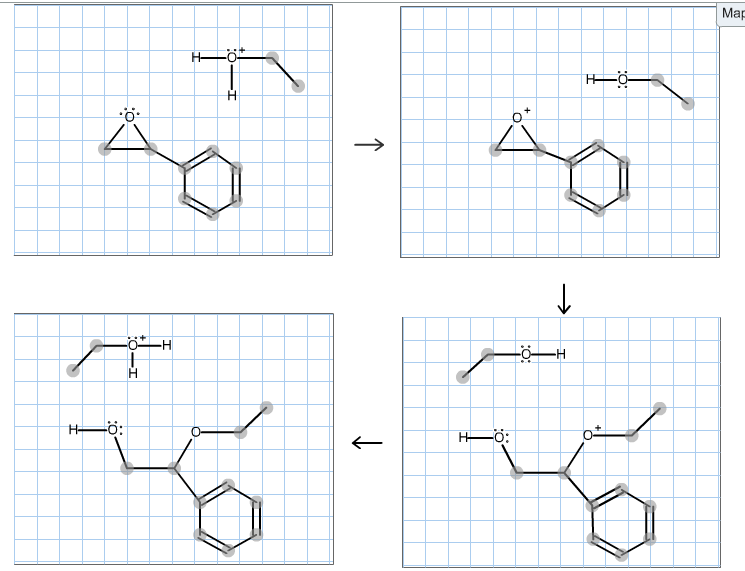
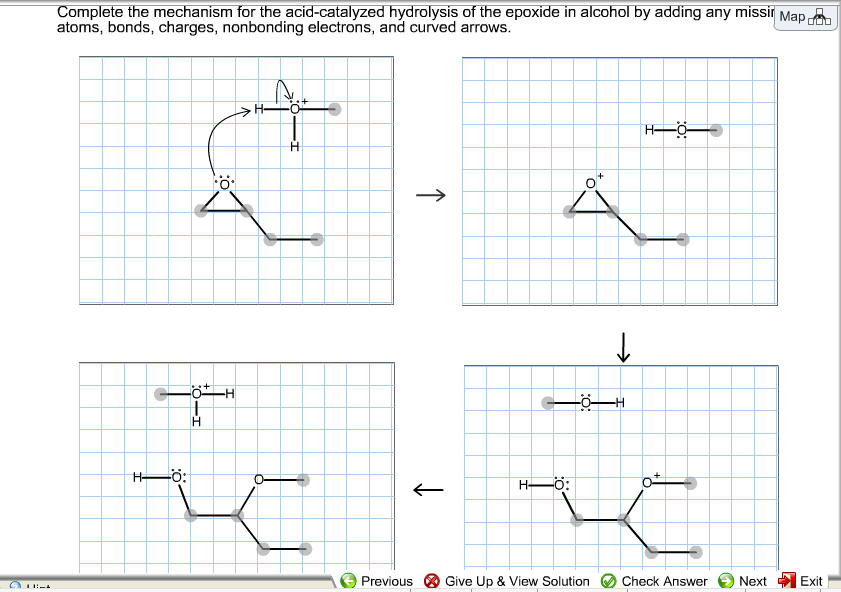
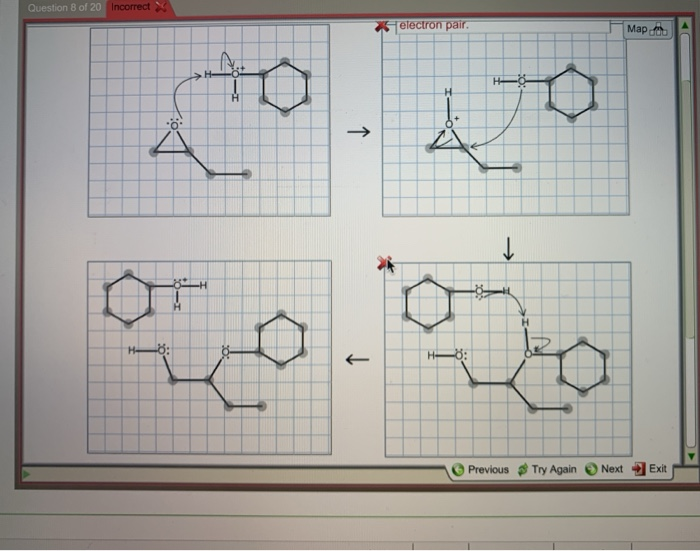
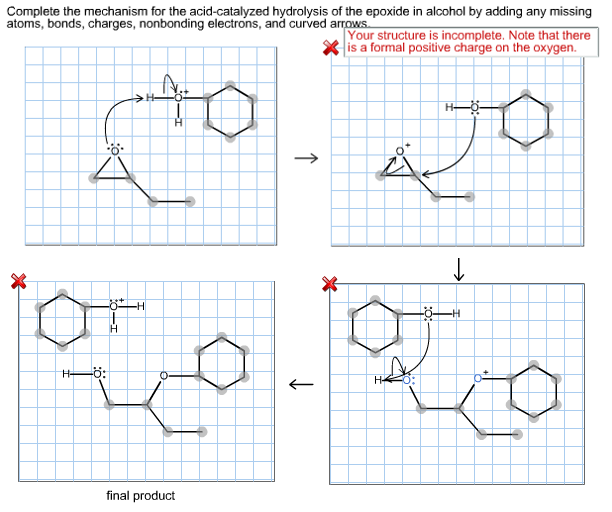
Complete the mechanism for the acidcatalyzed hydrolysis of the epoxide in alcohol by adding any missing atoms bonds charges nonbonding electrons and curved arrows. First the oxygen is protonated creating a good leaving group step 1 below. It uses ethyl ethanoate as a typical ester.
The result is a 12-diol. The electrons in one of the two C O bonds transfer to the O X breaking the bond and effectively transferring the positive charge to the carbon. Step 2 The alcohol executes a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl.
The carbonyl oxygen is protonated by the acid catalyst activating it toward a nucleophilic attack from the ethanol as illustrated below. OH protonated by second mole HBr Br- attacks alpha carbon releasing H2O. The C-O bond breaks to form an oxide ion on the adjacent carbon atom.
Protonation of the ester carbonyl makes it more electrophilic. Complete the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of theepoxide in alcohol by adding any missing atoms bonds chargesnonbonding electrons and curved arrows. MECHANISM OF THE ACID CATALYSED HYDROLYSIS OF ESTERS.
SN2 - Strong acid HBr protonates the ether oxygen which turns it into a better leaving group. This problem has been solved. THE MECHANISM FOR THE ACID CATALYSED HYDROLYSIS OF ESTERS This page looks in detail at the mechanism for the hydrolysis of esters in the presence of a dilute acid such as hydrochloric acid or sulphuric acid acting as the catalyst.
At this point note that the carbocation thus formed may rearrange. This creates a positively charged trivalent oxygen. In this reaction a primary alcohol is heated with an acid catalyst usually sulfuric acid.
Probably the best way to depict the acid-catalyzed epoxide ring-opening reaction is as a hybrid or cross between an S N 2 and S N 1 mechanism. We have seen that all the steps in the Fischer esterification are reversible and the equilibrium is shifted toward the ester product by using an excess of alcohol. A reminder of the facts.
First a proton from the acidic medium attacks the neucleophile O. Since we only have a weak nucleophile and a poor electrophile we need to activate the ester. Complete the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of the epoxide in alcohol by adding any missing atoms bonds charges nonbonding electrons and curved arrows.
This nature of the reaction allows to hydrolyze esters back into a carboxylic acid and alcohol when the water is now used in a large. Proton transfer from the acid catalyst generates the conjugate acid of the epoxide which is attacked by nucleophiles such as water in the same way that the cyclic bromonium ion described above undergoes reaction. Heterogeneously catalyzed oxidation of alkenes.
A mechanism for the acid catalysed hydrolysis of esters. According to a reaction mechanism suggested in 1974 at least one ethylene molecule is totally oxidized for every six that are converted to ethylene oxide. Next the Br ion attacks the methyl carbon in an SN2 reaction to give the alcohol and methyl bromide.
The mechanism for the hydrolysis of ethyl ethanoate. Complete the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of the epoxide in alcohol by adding any missing. All the steps in the mechanism below are shown as one-way reactions because it makes the mechanism look less confusing.
Acid and Base-Catalyzed Mechanism. There is also an acid catalyzed reaction which makes a symmetrical ether one in which the two alkyl groups attached to the oxygen are identical. The ester reacts with the water present to produce ethanoic acid and ethanol.
A molecule of water is lost and the ether is. The epoxide ion then picks up a proton from the water.
Complete The Mechanism For The Acid Catalyzed Chegg Com
Complete The Mechanism For The Acid Catalyzed Chegg Com
Complete The Mechanism For The Acid Catalyzed Chegg Com
Complete The Mechanism For The Acid Catalyzed Hydrolysis Of The Epoxied In Alcohol By Adding Any Missing Atoms Bonds Charges No Binding Electrons And Curved Arrow Image Src Reactions176392 Study Com
Complete The Mechanism For The Acid Catalyzed Chegg Com
Complete The Mechanism For The Acid Catalyzed Chegg Com
Complete The Mechanism For The Acid Catalyzed Chegg Com
Complete The Mechanism For The Acid Catalyzed Chegg Com
Complete The Mechanism For The Acid Catalyzed Chegg Com